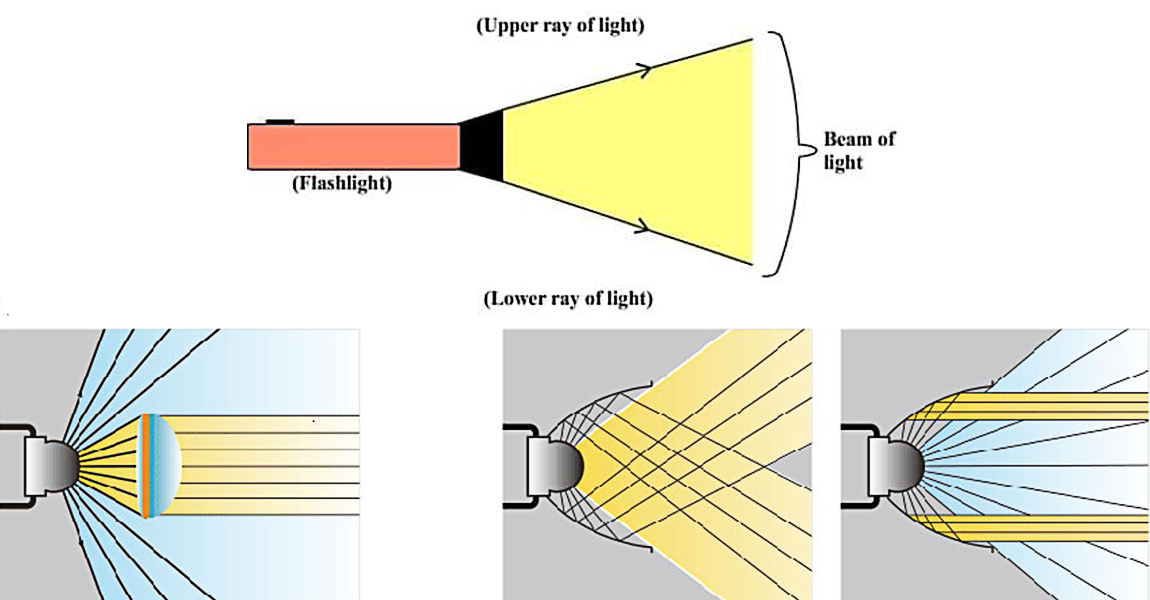
There is a lot of knowledge about the light beam of the torch. You will find that the light emitted by them has different light rays, different colours, and different illumination ranges. So how to choose and judge which kind of torch is you want?
Let’s look at the following factors:
1. Light beam of the torch
The light source illuminates the object by propagating light from the medium, and many tiny rays of light are generated in the process of propagation. Usually we can see the light from a window in a shady room, or the sun's rays from a dark cloud after a heavy rain. Many rays of light come together to form a beam, and all the rays in the beam can be parallel to each other.
Light can be spread out from a point, making the light wider and it can also be directed to a point from different directions. The light beam of the torch is diffused from the center of the torch to illuminate the object.
1.1. Hotspot

When you give a light to a smooth surface, you will find that the light will be divided into 2 different areas, the brightest area in the center is called Hotspot.
1.2. Spill
The not-so-bright light areas on the periphery of the central area, called Spills, are larger than the hotspot's brightest areas.
2. The light source of the torch
In the past, torchs used bulbs or HIDs to emit light, but now most of them are LED lights as illuminants.
By light source, we mean the type of LED light used by the torch.

Some LEDs have different colours, such as cold light, warm light, etc. (Click here to view: Different color temperatures of flashlights)
3. Torch Reflector
The LED light of the torch can illuminate further or larger area through the reflector.
Most of the spotlights and floodlights we usually say are produced by reflectors with widely different beam profiles.
The reflector generally works by its shape and surface texture.
3.1 Reflector shape
The larger the diameter of the reflector, the longer the reflector body and the farther the light it reflects will be projected, which is more suitable for long-distance focused lighting.
The smaller the diameter of the reflector, the shorter the reflector body, the wider the reflected light, and the more uniform the body surface can be illuminated, which is suitable for close-up lighting.
3.2 Reflector Surface Texture

The smoother the surface of the reflector, the farther the torch's beam will be cast.
There are two materials of the reflector: orange peel and smooth reflector, which are commonly known as OP and SMO
-
SMO
A smooth reflector will reflect a beam farther away, and you can see this kind of reflector on a torch that casts a very concentrated light.
It is mostly used in hunting, search, rescue, military tactics, etc. Because the light beam it produces satisfies these purposes, it also becomes a spotlight.
Olight spotlight torches: Warrior X Turbo, Warrior 3, Warrior X Pro, Warrior X 3, Javelot Pro 2, X9R Marauder.
-
OP
Because the texture of this reflector is very similar to an orange peel, it is called an orange peel reflector. OP textures help eliminate false lighting and create uniform lighting rays through diffuse reflections. Usually suitable for close-range lighting, also known as floodlights, generally used in daily household lighting, reading, study and work lighting. The daily carrying is more common.
It has names like Light Orange Peel (LOP) and Medium Orange Peel (MOP) to distinguish different texture details.
Olight floodlight torches: Seeker 3 Pro, Seeker 3, Seeker 2, Baton Pro.
4. TIR Lens
Here we can learn from the wiki that there are three types of lenses: Flat lens, Aspheric lens, and TIR optical lens.
There are two types of lenses related to the optical principle of the torch:
TIR lens: It has a total reflection paraboloid itself, no additional reflector is needed.
Flat lens: The lenses configured in front of the reflector are all flat lenses.
Olight's products using TIR Lens are: Warrior 3, Seeker series.
5.Light form / light image: floodlight, spotlight
Light form/light image, we refer to the image shape of the beam emanating from the torch. Some are straight beam images, some are wide-angle beam images, and some are combined beam images.
5.1.Spotlight: long-distance projection, focused beam image, throw light.

5.2.Floodlight: close-up lighting, Broad beam image

5.3. Combining throw and flood: It can not only see the near lighting, but also can accurately illuminate a certain object in the distance.

One of the principles of combining spotlight and floodlight is to adjust the focal length. That is, change between spotlight and floodlight by adjusting the distance between the convex lens and the lamp bead.
The main ways to adjust the focal length include rotating and elongation-shrinking. For both spotlight and floodlight are taken into account, this combined light torch can be widely used indoors and outdoors, such as hiking, camping, night riding, home, mountain climbing and night fishing.
Olight's spotlight and floodlight torches: Marauder 2, X9R Marauder. (Click here: Comparison between Olight X9R Marauder and Marauder 2 Flashlights)
The design principle of Olight combined light torch does not use this method, but adds spotlight and floodlight lamp beads in 2 different positions. By turning on different switches, you can choose whether it is spotlight or floodlight.
6. Other beam colours of the torch
LED torch can also emit different colours in addition to the colour of their own bulbs (The picture above is the Olight Freyr Multi-Colour Torch, click on the picture or here to view the product).
Some colours may come with the lenses themselves for they have different colours filters. And different colours of light are used for different purposes, not just to look beautiful.
6.1. Red: Red is probably the most common LED colour. I have a headlamp that I carry with me when camping and backpacking, and it has several different colour settings, including a red LED. At first I had no idea what the red light was for, so I never used it before. However, it turns out that red lights can protect your night vision, so they're perfect for camping, hiking, backpacking, hunting, or anything for that matter. Some say they are also great in smoky environments.
6.2. Blue: Blue light is commonly used by hunters when tracking the blood of wounded animals. Blood is hard to spot under white light (apparently red light), but easier to see under blue light. Using blue light in fog is also better than white light.
6.3. Green: Green lights are said to be useful to hunters and fishermen as they are less likely to scare their prey. Some say this is because some animals have a harder time seeing green light than white light or other colours of light.
6.4. Ultraviolet rays: Ultraviolet rays (when used in torches) are often used to charge light-emitting items such as compasses or dials.
If you want to see more about multi-color flashlight beams, click here!